BYTECURVE RESOURCES
Driving Violations Documented By Stop-Arm Cameras: Underscoring Need for Deterrence
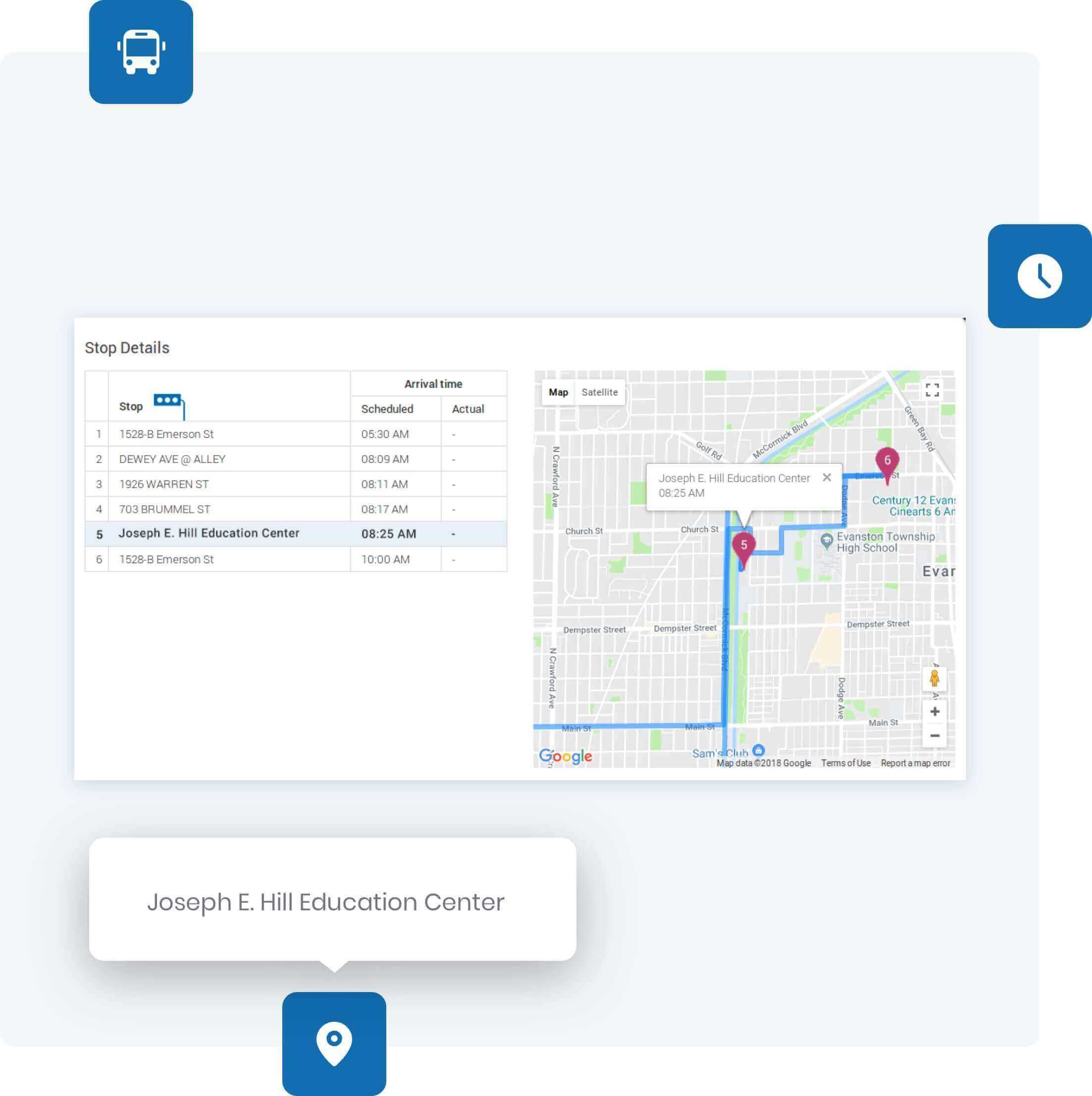
Our School Bus Operating platform arms your team with the information they need to improve decision making around safety, reducing costs, and being more efficient each day.
Trusted by dozens of public and private student transportation fleets to improve how they do business.
Trusted by the Finest Names in School Bus Transportation
Stop-Arm Cameras Document Thousands of Driving Violations, Underscoring Need for Deterrence
The numbers are enough to stop you in your tracks.
The hope is that they’ll do just that to anyone thinking about passing a school bus with its stop arm activated.
In Yonkers, just north of New York City, the statistics from 10 months’ worth of data since the school district started using stop-arm cameras on its fleet of 180 school buses tell a sobering story.
Since January, when Yonkers became the largest school district in New York to use stop arm safety technology, thousands of violations have been issued.
“Having 18,000 instances where people were passing school buses is completely unacceptable,” said Yonkers Mayor Mike Spano, according to WABC-TV (ABC) in New York City.
The cameras, which begin recording while the bus’s stop arm is extended, have provided school officials with visual evidence of dangerous driving that might otherwise go unreported.
“We wouldn’t have that (evidence) other than what a driver would report. This actually substantiates the driver’s claims as they try to keep our kids safe (and) pay attention to the kids on the bus while also monitoring what’s going on on the road,” said Yonkers Schools Superintendent Anibal Soler Jr., per the WABC-TV report.
With fines ranging from $250-$300 per violation, that adds up to some serious money for both the city and the company that supplies the cameras and reviews the videos. The cameras are provided for free.
Officials say the goal is not to make money as much as it is to raise awareness and change behavior, adding that 92 percent of offenders do not commit a second violation, per the report from the local ABC affiliate.
A fact sheet from 2023 National School Bus Safety Week, provided by the U.S. Department of Transportation’s National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), highlights just how dangerous the illegal passing of a school bus can be and provides a glimpse of how often it happens:
- In the National Association of State Directors of Pupil Transportation Services (NASDPTS) 2022 Stop Arm survey, 79,859 school bus drivers reported that 51,593 vehicles passed their buses illegally on a single day during the 2020-21 school year. Throughout a 180-day school year, these sample results point to more than 41.8 million violations per year among America’s motoring public.
- The most dangerous part of the school bus ride is getting on and off the school bus.
- The school bus loading and unloading area is called the “Danger Zone.” Specifically, this is any side of the bus where a child may not be seen by the bus driver and, therefore, is in the most danger. These areas include:
- 10 feet in front of the bus, where the driver may be sitting too high to see a child
- 10 feet on either side of the bus, where a child may be in the driver’s blind spots
- Behind the school bus
- Young children are most likely to be struck because they:
- Hurry to get on and off the bus
- Act before they think and have little experience with traffic
- Assume motorists will see them and wait for them to cross the street
- From 2011 to 2020, there were 1,009 fatal school transportation-related crashes, and 1,125 people of all ages were killed in those crashes — an average of 113 fatalities per year.
- From 2011 to 2020, there were 1.6 times more fatalities among pedestrians (183) than occupants of school buses (113) in school-bus-related crashes. A total of 218 school-age children (18 and younger) died in school-bus-related crashes during that period, either as occupants of school buses or other vehicles, or on foot or bike. Of the 218 deaths, 85 were children who were walking.


Bytecurve360 delivers a transformative operational experience.
Some of the most essential features include:
- Better Driver communications so that employees can check in/out remotely, view their schedules and receive messages on their smartphones.
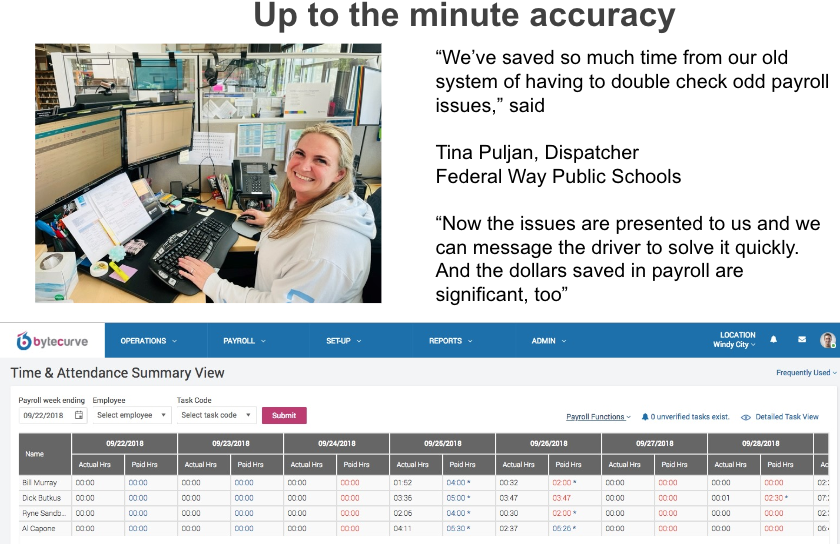
- Easier payroll management so that you no longer have to manually calculate employee guarantees/contracts and overtime.
- Simpler management of daily operations, including assigning/reassigning drivers and vehicles, using real-time integration with GPS and routing systems. This allows all stops to be easily be rerouted when a bus breaks down or a driver can’t come in.
To further illustrate the point, NASDPTS has a site that provides statistics on stop-arm violations and videos that show how dangerous the practice of passing a stopped school bus can be.
The following video was developed by WNCN in Raleigh, North Carolina, as a public service in conjunction with the NC Department of Public Instruction: #Brake4Buses Public Service Announcement (YouTube)
Georgia’s Cobb County has one of the nation’s longest-standing stop-arm camera programs, which was launched following a tragic 2009 incident in which a kindergarten student was struck and killed by a motorist while exiting her bus.
The district’s response would include extensive efforts to warn the public about stop-arm running and the installation of cameras to catch those who would continue to illegally pass the district’s buses.
“You don’t look at it the same once you’ve had a fatality,” Rick Grisham, former executive director of transportation for Cobb County School District, said of the stop-arm running issue. “That hit home for us—it has to stop.”
From preventing dangerous traffic violations to monitoring student behavior, the right technology can help school bus drivers enhance their safety protocols, ensuring that children are protected during their daily commute.
As the only software solution that merges GPS Fleet Tracking and routing data into a new solution, Bytecurve360 is the fastest-growing technology serving the student transportation industry thanks to its ability to significantly improve:
- Payroll operations, including the streamlining of different pay codes and jobs or tasks between and among staff members
- Dispatching operations, including the ability to alter routes, runs and tasks in real-time to respond to later and/or absent drivers
- Real-time app-powered communications, including the ability for drivers in the field to respond to route changes via the app
Stop-arm cameras are increasingly being adopted by school districts as a tool to deter illegal passing and hold violators accountable.
The question remains: do these cameras actually make a difference? Can they truly protect schoolchildren and change driver behavior over time?
In this article, we’ll explore how stop-arm cameras work, how they protect schoolchildren, and whether or not they successfully deter drivers from making dangerous choices.
School bus safety has been a priority for communities and governments for decades. With millions of students relying on school buses to travel to and from school each day, ensuring their safety is paramount. While buses themselves are equipped with an array of safety features—flashing lights, reflective markings, and stop arms that signal drivers to stop—one persistent problem continues to put students at risk: drivers illegally passing stopped school buses.
To combat this growing issue, school districts across the country have turned to technology, particularly school bus stop-arm cameras, as a solution.
These cameras are designed not only to catch violators but, more importantly, to act as a deterrent against unsafe driving behaviors around school buses.
In this article, we’ll explore the technological capabilities of stop-arm cameras, how they work to prevent violations, and their effectiveness as a deterrent in enhancing student safety.
The Problem: Illegal Passing of School Buses
Despite the bright yellow color of school buses, flashing red lights, and the extended stop-arm signaling drivers to stop, illegal passing of school buses remains a widespread problem.
As part of its 12th-annual survey on illegal passing of school buses, NASDPTS said approximately 26.4% percent of the nation’s school bus drivers from 35 states throughout the country and the District of Columbia participated in a one-day survey to report motorists who passed their stopped school buses. In the survey, 98,065 school bus drivers reported that 66,322 vehicles passed their buses illegally on a single day during the school year.
“Adjusting for 100% of the school bus drivers in the U.S., we would have seen just over 251,000 illegal passings,” NASDPTS said. “Projected across a 180-day school year, these sample results point to more than 45.2 million violations per year among America’s motoring public. As the projected violations for the 2022-2023 school year were 43.5 million, we continue to see the problem of the illegal passing of stopped school buses increase.”
The reasons for illegal passing vary from driver ignorance to deliberate disregard for the law, but the consequences are dire. When a driver passes a school bus, especially when students are boarding or disembarking, it increases the risk of severe injury or even death.
In many instances, the bus driver or witnesses are unable to identify the violator, allowing dangerous driving behavior to go unpunished.
This is where school bus stop-arm cameras come in—not only to hold drivers accountable but also to prevent these violations from happening in the first place.
What Are School Bus Stop-Arm Cameras?
School bus stop-arm cameras are external cameras installed on school buses, specifically designed to capture images or videos of vehicles that illegally pass the bus when it stops with its stop-arm extended and lights flashing.
These cameras are strategically placed on the side of the bus to have a clear view of both the front and rear of any vehicles that might pass the stopped bus.
While the basic premise of stop-arm cameras is simple, the technology behind them is sophisticated and evolving, with the primary goal of deterrence through monitoring and enforcement.
How Stop-Arm Cameras Work
The process of capturing violations with stop-arm cameras is highly automated and precise. Here’s a breakdown of how these cameras function:
- Camera Activation: The cameras are automatically activated when the bus driver deploys the stop-arm, signaling that students are either boarding or exiting the bus. The flashing red lights also signal the cameras to begin recording.
- Video and Image Capture: Stop-arm cameras record video footage of vehicles that fail to stop when the bus is loading or unloading students. These cameras are equipped with high-definition video capabilities, allowing them to capture clear images of the vehicle, including the license plate, make, model, and even the driver’s face in some cases.
- Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR): Modern stop-arm cameras are often integrated with ALPR technology, which allows the system to automatically detect and record the license plate number of the violating vehicle. This information is critical for law enforcement to issue citations quickly and accurately.
- Data Transmission: Once a violation is recorded, the video footage and data (such as the vehicle’s license plate number, the time and location of the violation, and images of the vehicle) are transmitted to local law enforcement or third-party services that review the footage. If the violation is confirmed, a citation is issued to the driver.
- GPS Integration: Many stop-arm camera systems are also integrated with GPS technology to log the exact location of each violation. This data can be useful in identifying hotspots where violations frequently occur, allowing school districts and law enforcement to target those areas for additional safety measures.
The Deterrence Effect: How Stop-Arm Cameras Prevent Violations
The primary goal of stop-arm cameras is not to catch and penalize drivers after the fact, but to deter illegal passings from occurring in the first place.
Here’s how these cameras serve as an effective deterrent:
1. Creating a Culture of Accountability
One of the key factors in stop-arm camera deterrence is the perception of enforcement. When drivers know that their actions are being monitored by a camera system, they are more likely to comply with traffic laws.
This phenomenon is similar to the effect of red-light cameras or speed cameras in urban areas: drivers are aware that they are being watched and therefore adjust their behavior to avoid fines and penalties.
As stop-arm cameras become more widespread and publicized, drivers are more likely to think twice before illegally passing a school bus. The presence of these cameras sends a clear message: there are consequences for breaking the law, and those consequences are unavoidable.
2. High Visibility of Cameras
Many school buses equipped with stop-arm cameras have signs or decals indicating that the bus is monitored by cameras. These visible warnings serve as an immediate reminder to drivers that they are being watched and that any illegal passing will be recorded.
Much like the deterrent effect of security cameras in public places, the mere presence of visible enforcement tools prompts drivers to comply with the law.
When combined with public awareness campaigns and educational efforts by schools and law enforcement, these signs amplify the deterrence factor.
3. Consistent and Reliable Enforcement
Prior to the implementation of stop-arm cameras, enforcing school bus stopping laws was inconsistent. Bus drivers could report violations, but without concrete evidence or law enforcement presence, many violators would go unpunished.
Even if a driver noted the license plate number of the vehicle, it was often difficult for law enforcement to pursue the case without visual proof of the violation.
Stop-arm cameras provide a solution by offering continuous and reliable enforcement. The cameras are always there, capturing every violation with clear video evidence.
This consistency removes any ambiguity about whether or not a driver will face consequences, further reinforcing the deterrence effect.
4. Financial and Legal Consequences
The penalties for illegally passing a stopped school bus can be steep, especially in areas where stop-arm cameras are in use. In many states, drivers who are caught on camera violating school bus stopping laws face fines ranging from $250 to $1,000, depending on the severity of the violation and whether it is a repeat offense.
In some jurisdictions, violators also receive points on their driver’s license, which can lead to higher insurance premiums or even license suspension if too many points accumulate.
The combination of financial penalties and legal consequences acts as a powerful deterrent, making drivers think twice before risking a violation.
Technological Capabilities of Modern Stop-Arm Cameras
The deterrent effect of stop-arm cameras is greatly enhanced by the advanced technology behind them. Let’s explore some of the cutting-edge capabilities of modern stop-arm cameras and how these features contribute to their effectiveness:
1. High-Resolution Video and Image Capture
Modern stop-arm cameras are equipped with high-definition video capabilities, ensuring that the footage they capture is clear and detailed.
This is particularly important for identifying license plate numbers, vehicle make and model, and the driver’s appearance. The quality of the video ensures that violators cannot contest the citation due to poor image quality.
Some camera systems even offer night-vision capabilities, allowing them to capture clear footage in low-light conditions, such as during early morning or late afternoon bus routes.
2. Wide-Angle Coverage and Multi-Lane Monitoring
To increase their effectiveness, many stop-arm cameras are designed to cover multiple lanes of traffic. This is especially useful for buses that stop on multi-lane roads, where vehicles approaching from both directions must stop.
Wide-angle lenses allow the camera to capture vehicles from various angles, ensuring that no violator escapes detection.
This multi-lane monitoring capability is crucial for buses that operate on busy roads or highways, where the risk of illegal passing is higher.
3. Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR)
One of the most powerful features of modern stop-arm cameras is ALPR technology. As mentioned above, ALPR systems use optical character recognition to automatically detect and record the license plate number of any vehicle that passes the stopped bus illegally.
This automation streamlines the enforcement process by eliminating the need for manual review of footage, allowing citations to be issued more quickly and accurately. It also reduces the possibility of human error in identifying violators.
4. GPS Integration for Location Tracking
Many stop-arm camera systems are integrated with GPS technology, allowing them to record the exact location of each violation. This data is valuable for school districts and law enforcement agencies, as it helps them identify areas where illegal passing is more common. With this information, they can implement additional safety measures, such as relocating bus stops or increasing police presence in high-risk areas.
5. Real-Time Data Transmission and Citation Processing
Some stop-arm camera systems are connected to real-time data transmission networks, allowing them to send violation footage and data directly to law enforcement or third-party citation processing centers. This reduces the time between the violation and the issuance of a citation, making the enforcement process more efficient and effective.
Real-time data transmission also allows for faster response times in cases where immediate intervention is necessary, such as in situations where the violator poses an ongoing threat to student safety.
Effectiveness of Stop-Arm Cameras: Real-World Results
Stop-arm cameras have already been deployed in numerous school districts across the United States, and the results have been promising. In many cases, districts have reported a significant reduction in the number of illegal passing incidents after installing stop-arm cameras.
The success of the program in Cobb County prompted other districts in Georgia to adopt similar technology, further improving student safety across the state.
School bus stop-arm cameras have proven to be an essential tool in preventing dangerous driving behavior and ensuring the safety of students. By providing continuous, reliable enforcement and acting as a visible deterrent, these cameras discourage drivers from illegally passing stopped school buses, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
As more school districts adopt stop-arm camera technology, the hope is that violations will continue to decrease, creating a safer environment for students as they travel to and from school each day. The power of deterrence is clear—when drivers know they are being watched and that violations carry real consequences, they are far more likely to comply with the law, ensuring that every student’s journey is a safe one.

Integrated Student Transportation Software

If you are in the market for a school bus driver scheduling software, here’s what to look out for
- The application should feature a user-friendly design to enable administrators, drivers, and parents to understand and navigate the system. It should be cloud-based and be supported by U.S.-based support team who appreciate the unique demanding environment of a school bus fleet.
- The platform should include ongoing and comprehensive training and support for all users to guarantee they’re comfortable with the tool and can use it effectively. Bytecurve features ongoing support from our team of school bus operations experts.
- The school bus driver scheduling software platform you eventually select should commit to continuous updates and maintenance to ensure it remains current and devoid of bugs or glitches. Bytecurve is founded by innovators who will never stop improving the platform based on the needs and wants of their customers and school bus fleet operators.
- The app should be flexible and customizable to tailor it to the unique needs of each school or district. Bytecurve will work with each district or contract to build their tailored solution that meets their unique requirements.
- The software should be capable of integrating with other related tools like student information systems to guarantee accurate and up-to-date data is being used to create and manage driver schedules. Bytecurve has integrations with all of the major routing and GPS fleet tracking solutions so that virtually any school bus fleet can enjoy the benefits of the transformative technology.


Secure
Only authorized employees will be able to access DriveOn based on a customer specific access code. This code can be turned off as needed by an authorized administrator.

User friendly
DriveOn is easy to use with a simple, smart interface.
Available on both iOS and Google Play stores.