“Bytecurve makes our payroll process seamless with reduced time and paperwork,”
-Jennifer Idlette, Transportation Director, Indian River School District
Buses Served
Districts and Contractors
Payroll Processed
Turning School Buses Into Rolling Batteries
How V2G Technology Can Benefit School Districts and Local Utilities
Almost a quarter of a century ago, a modest California company called AC Propulsion tried to answer a not-so-simple question:
Could an electric vehicle transmit electricity back to the power grid?
First explored as a concept by researchers from the University of Delaware in 1997, the concept of vehicle-to-grid technology, or V2G, “gained traction in the late 1990s when California’s landmark zero-emission-vehicle (ZEV) mandate went into effect and compelled automakers to commercialize electric cars,” according to an article in IEEE Spectrum, the flagship publication of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
AC Propulsion’s two-seater sports car, the Tzero, “featured bi-directional charging capability,” a feature that had been implemented to “give drivers the ability, in an emergency, to charge another EV (electric vehicle),” IEEE Spectrum wrote in another article on the history of EVs and V2G technology.
As IEEE Spectrum’s reporting explained,
“In V2G, environmental-policy wonks saw a potent new application of the EV that might satisfy many interests. For the utilities, it promised an economical way of meeting rising demand for electricity. For ratepayers, it offered cheaper and more reliable electricity services. Providers of EVs would have a new public-policy rationale backing up their markets. And EV owners would become entrepreneurs, selling electricity back to the grid.”
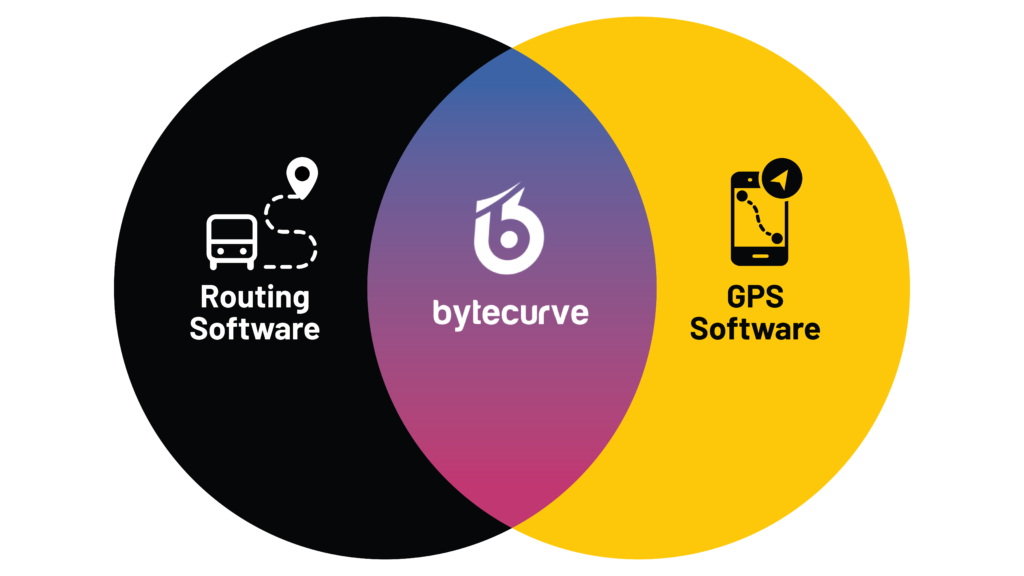
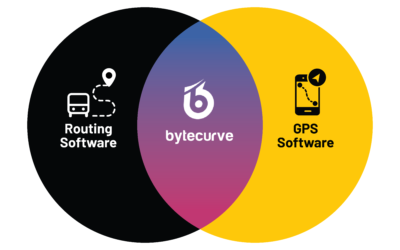
Bytecurve Helps Improve Routing, GPS, and Payroll Systems
While the California power crisis and rolling blackouts of the early 2000s underlined a need for V2G, as did the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan, which left 4.4 million homes without power, IEEE Spectrum said the concept was not seriously tested by the market until 2010, when the release of the Nissan Leaf “heralded the start of widespread, commercially available electric vehicles.”
The rise of Tesla and other EV makers, including those in China, have provided additional impetus behind the EV market and, as IEEE Spectrum put it, “revived prospects for the EV as a power-grid resource.”
“For the utilities looking for ways to store power for later use, all those shiny new EVs might look like rolling batteries that they can not only charge but also draw power from when demand exceeds supply,”
IEEE Spectrum continued.
In a measure of how far V2G has come after a number of false dawns over the previous quarter century, consider the recent partnership between the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory and Lion Electric, North America’s largest manufacturer of medium-sized and heavy-duty EVs.
Together, they are “partnering to explore the integration of EVs into the power grid through Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology,” according to a recent press release. “By harnessing the power of Lion Electric’s zero-emission buses and trucks, this collaboration seeks to transform vehicles into grid assets capable of supporting grid stability and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
Hearkening back to AC Propulsion’s trailblazing efforts, the partnership between Argonne and Lion emphasized that bi-directional chargers are “central to the success of V2G.”
Bi-directional chargers, they said, “facilitate the seamless exchange of energy between EVs and the grid. Argonne’s SpEC Module, coupled with Lion Electric’s LionC all-electric school bus, demonstrates the practical application of V2G technology by successfully conducting a dynamic bi-directional charging session.
“This collaboration showcases the LionC’s potential to generate revenue for school districts, provide power during emergencies, and alleviate strain on local electricity infrastructure. Through initiatives like these, Argonne and Lion Electric are driving towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.”

Can Bus Batteries Be Used to Help Local Utilitites Provide a More Sustainable Future?
Potential for Significant Benefits
V2G technology in school buses has the potential to bring significant benefits to both local school districts and the surrounding electricity infrastructure.
By allowing school buses to not only charge from the grid but also send electricity back to it, V2G technology enables school buses to function as mobile energy storage units. This can provide cost savings, revenue opportunities, and help stabilize the electrical grid, particularly during peak demand periods.
Here’s how this innovative technology can help both local school districts and the local electricity infrastructure:
Cost Savings and Revenue Generation for School Districts
School districts often face tight budgets, and energy costs can be a significant expenditure. V2G-equipped school buses can provide financial benefits in two ways: lowering electricity costs and generating revenue through energy sales back to the grid.
- Lower Energy Costs: School buses generally remain idle for large portions of the day, especially during non-school hours, nights, and weekends. During these periods, V2G technology allows buses to charge when electricity rates are low (off-peak hours) and return energy to the grid during peak times when electricity demand—and prices—are high. By optimizing when they pull energy from the grid and when they return it, school districts can reduce overall energy expenses.
- Revenue Opportunities: School districts can sell excess energy stored in bus batteries back to the grid during peak demand periods, generating revenue. Utilities often offer incentives or pay premiums for energy fed into the grid during high-demand times, especially when they need extra capacity to prevent blackouts or stabilize the grid.
This dual benefit—reduced energy costs and new revenue streams—can offset the costs of purchasing and maintaining electric school buses, making them more affordable in the long run.
This can be particularly valuable as school districts across the country transition to electric buses to meet environmental standards and reduce emissions.
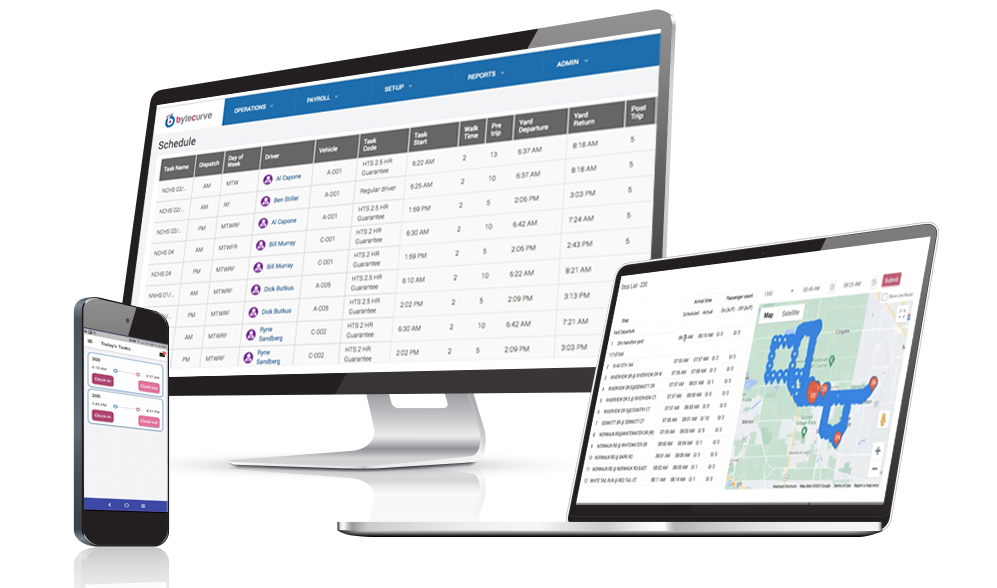
As the only software solution that merges GPS Fleet Tracking and routing data into a new solution, Bytecurve360 is the fastest-growing technology serving the student transportation industry thanks to its ability to significantly improve:
- Payroll operations, including the streamlining of different pay codes and jobs or tasks between and among staff members
- Dispatching operations, including the ability to alter routes, runs and tasks in real-time to respond to later and/or absent drivers
- Real-time app-powered communications, including the ability for drivers in the field to respond to route changes via the app
Enhanced Grid Stability and Support for Local Infrastructure
For the local electricity infrastructure, V2G technology offers a way to bolster grid resilience, improve energy efficiency, and help manage electricity demand, especially during times of stress on the grid.
- Grid Stability: During peak hours when the demand for electricity is high (such as during hot summer days or cold winter evenings), local utilities may struggle to supply enough power to meet demand. V2G-equipped school buses can provide backup energy during these times, helping to balance the grid and avoid blackouts or brownouts. By discharging electricity from their batteries back into the grid during high-demand periods, school buses act as distributed energy resources (DERs) that contribute to a more resilient and reliable grid.
- Support for Renewable Energy: Many regions are shifting toward renewable energy sources like solar and wind. While these sources are cleaner, they can be intermittent, leading to supply fluctuations. V2G technology in school buses can help bridge the gap by storing excess renewable energy during times of low demand and feeding it back into the grid when needed. For example, during a sunny day, excess solar energy can be stored in bus batteries, then discharged into the grid during the evening when solar power generation drops off.
- Reducing Peak Demand Strain: During peak demand hours, utilities often have to rely on costly and polluting “peaking plants” to meet demand. V2G school buses can reduce the need for these plants by providing a decentralized energy source. By feeding stored energy back into the grid during peak periods, buses help reduce the strain on the grid and lower the overall cost of electricity generation, which can benefit all ratepayers.
Environmental Benefits for Both Districts and Communities
In addition to economic and grid benefits, V2G technology in school buses supports environmental goals that are important to both school districts and local communities.
- Reduced Emissions: Electric school buses equipped with V2G technology help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, especially when paired with renewable energy sources. Traditional diesel-powered buses contribute to air pollution, which can be harmful to both students and the wider community. By switching to electric buses with V2G capabilities, school districts can play a role in reducing their carbon footprint and promoting cleaner air.
Supporting a Transition to Clean Energy: School buses using V2G technology can facilitate the broader adoption of renewable energy in the local community by helping stabilize the grid, making it easier for utilities to incorporate solar, wind, and other clean energy sources. The ability to store and discharge energy when needed helps balance the variable nature of renewable energy and makes it more reliable for widespread use.
Emergency and Backup Power for Local Communities
Another critical advantage of V2G technology is its potential to provide backup power during emergencies. School buses can serve as mobile power sources for critical facilities or neighborhoods during power outages caused by extreme weather events or other disruptions.
- Backup Power for Schools and Community Centers: In times of natural disasters or power grid failures, V2G-enabled school buses can provide backup power to schools, community centers, or emergency shelters. These buses can be deployed to supply electricity for lighting, heating, and communication systems, ensuring that essential services remain operational during a crisis.
- Emergency Response Support: Beyond schools, V2G buses can also support broader emergency response efforts by providing power in areas affected by power outages. For example, during a hurricane or winter storm that causes widespread blackouts, these buses can be mobilized to deliver power where it is needed most, enhancing the community’s resilience to such events.
Timing and Practical Considerations for Implementation
While V2G technology offers considerable benefits, its implementation does require careful planning and collaboration between school districts, utilities, and policymakers.
- Upfront Costs: One of the biggest challenges is the initial cost of electric school buses and the infrastructure required to support V2G operations, such as bidirectional chargers. However, these costs are often offset over time by the financial savings and revenue opportunities V2G technology provides. Additionally, government grants and incentive programs aimed at reducing carbon emissions and improving energy efficiency can help fund these investments.
- Coordination with Local Utilities: For V2G to be successful, school districts must work closely with local utility companies. This partnership ensures that buses can be seamlessly integrated into the grid and that the necessary infrastructure is in place for energy transfer. Utilities may also need to adapt their energy management systems to effectively use the energy stored in bus batteries.
- Battery Health and Lifespan: Concerns about battery degradation can be mitigated by intelligent energy management. V2G systems are designed to avoid deep discharges and charge cycles that would shorten battery life, ensuring that the buses remain operational for their primary purpose of transporting students.
V2G technology in school buses provides numerous benefits for both local school districts and the surrounding electricity infrastructure.
By enabling buses to function as mobile energy storage units, school districts can reduce energy costs, generate revenue, and contribute to a more reliable and resilient electrical grid.
V2G technology helps stabilize the grid during peak demand periods, supports renewable energy integration, and offers backup power in emergency situations.
For school districts, it represents a valuable investment in both financial sustainability and environmental responsibility, making V2G-equipped electric school buses a win-win solution for communities.
Integrated Student Transportation Software
About Bytecurve
Founded in 2018 by GP Singh after many years on the frontline of student transportation operations with one of the country’s largest private student transportation providers, Bytecruve is designed as the 360 view of operations.
By blending routing and GPS fleet tracking data, and adding a payroll capability as well as mobile app for two-ways communications between dispatch and drivers, Bytecurve 360 has created a new category for student transportation excellence: the dispatch command center.
“We believe many school bus operators still don’t appreciate all the potential improvments they can deliver by taking two powerful yet independent systems and merging them into a new layer of visibility and action,” Singh said. “We’re integrated with all the major providers of routing systems and GPS fleet tracking so virtually any school district with both systems can take advantage of our transformative technology.”
Trusted by dozens of districts across North America, more than 40,000 school bus rely on Bytecurve technology to improve their efficiency and safety.
“I know from first hand experience what school bus fleet leaders need to perform at their best, and we work tirelessly on our product and with our customers to deliver this experience so they can know they are investing in the safest and most efficient fleet.”